Describe and Give an Example of a Membrane Channel
Describe and give an example of diffusion. Decreasing temperature hts can caese 0 be-cane solid b.
3 4 The Cell Membrane Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Tap again to see term.
. An inner ear hair cell allows potassium. Describe this model and then cite two lines of evidence that were inconsistent with it. Classify the phrases based on whether they describe or give an example of simple diffusion facilitated diffusion transport primary active transport or secondary active transport.
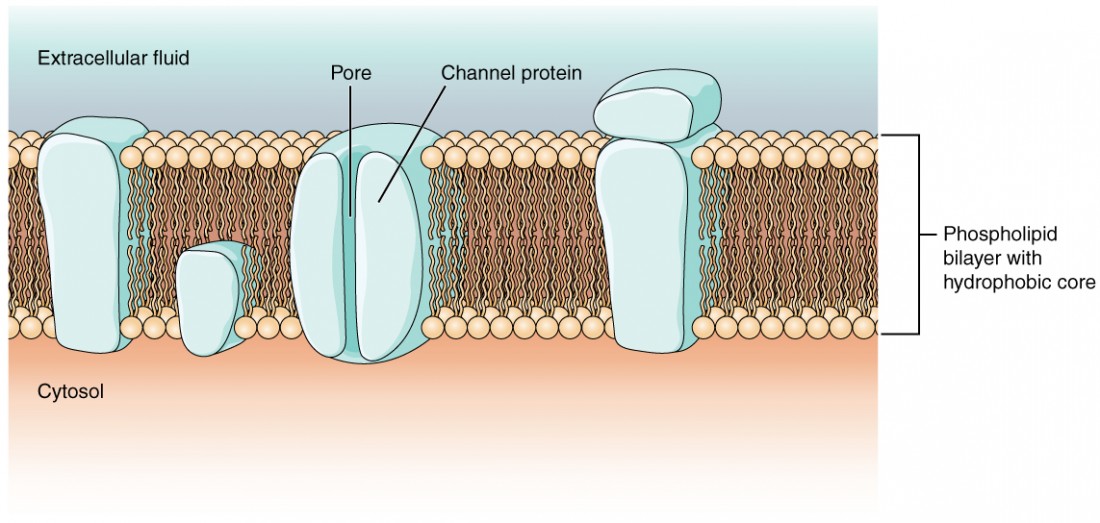
Describe the role of the K leak channel. The membrane has channel proteins embedded. Because it is non-polar it can easily slip through the lipid bilayer.
School Fortis College. A channel protein in the plasma membrane of a plant animal or microorganism cell that specifically facilitates osmosis the diffusion of free water across the membrane diffusion the spontaneous movement of a substance down its concentration or electrochemical gradient from a region where it is more concentrated to a region where it is less concentrated. For this specialized carrier protein molecules help in moving substances from one side of the membrane to the other.
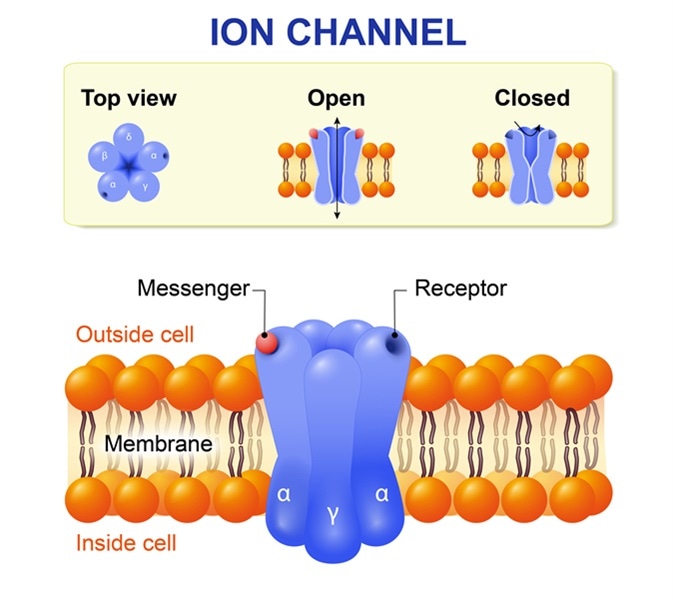
A neuron allows sodium ions to enter the cell down their concentration gradient using a membrane channel. Describe and give an example of a membrane channel a Membrane channels are a. Identify the following general structural components of the plasma membrane.
Pumps drugs out of the cell before the drug can exert its effects. Relating to active transport. These channels are open and close in response to change in electrical potential across the cell membrane.
An erythrocyte low on glucose replenishes its supply using a membrane protein to transport glucose down its concentration gradient. This greater conductance is thought to be conferred by the cell membranes proteins. Examples of substances using this route are glucose amino acids.
Ion channels have been extensively studied in excitatory cells like neurons and muscle fibers since the movement of ions across the membrane is an integral part of their function. What are ion channels. In an experiment a scientist separates two bodies of water with a thin phospholipid membrane such as that found in a cell.
Protein channels in the plasma membrane that have ion selectivity and are not continuously open. A neuron allows potassium ions to leave the cell down their concentration gradient using a membrane channel. What does specificity mean in relation to these proteins.
Transport of H into the lysosome driven by hydrolysis of ATP Select Transport of glucose into. Describe the structure of MDRs. Diffusion with the help of channel proteins.
A liver cell takes in ethanol molecules directly through its plasma membrane after the ingestion of alcohol. Compare channel proteins with carrier proteins. What will pass through the membrane with difficulty.
What are transport proteins. Partial Question 1 05 1 pts Q1. B cil are Phospholipids move layer and Hip phesmclipjd 04.
What is an. Give examples of materials involved in the following types of transport. An example of this occurs in the kidney where both forms of channels are found in different parts of the renal tubules.
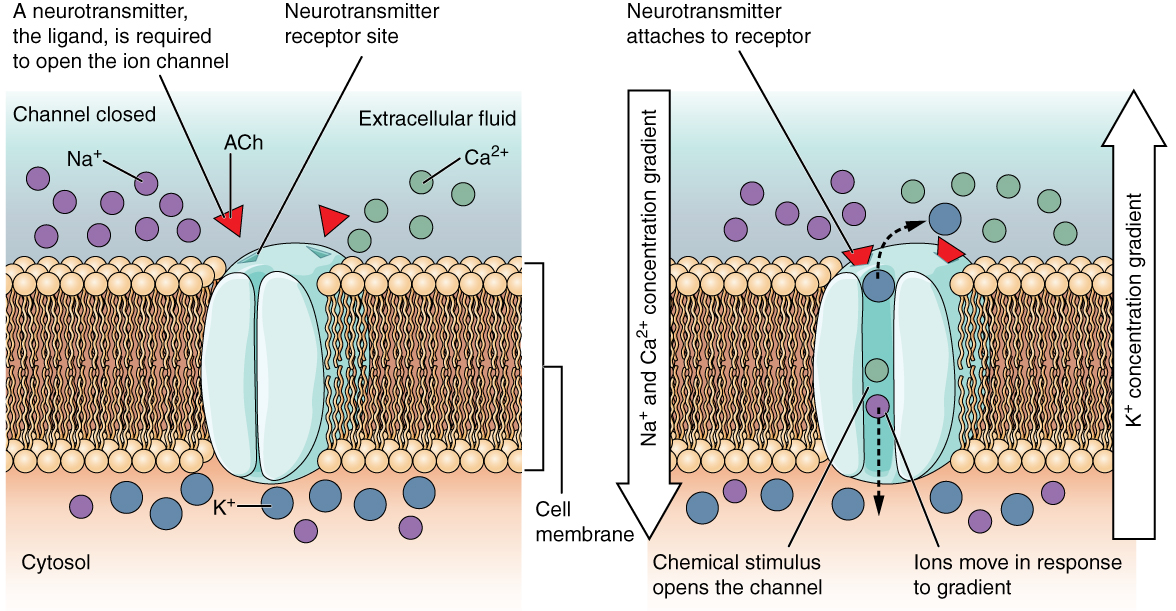
Describe the difference in function of ABC transporters in proks and euks. Cells involved in the transmission of electrical impulses such as nerve and muscle cells have gated channels for sodium potassium and calcium in their membranes. A channel protein serves as a tunnel across the membrane into the cell.
When the substance molecules bind the carrier protein changes its shape so that the molecules move to the other end of the channel in the protein. Describe ion channel receptors explain how they can be activated by signal molecules and give an example of this process in humans. These channel proteins form pores on the lipid bilayer that can be either in the open or closed conformation depending on the electrical potential of the cell and.
Which statements describe examples of facilitated diffusion. An epithelial cell absorbs amino acids against their concentration gradient using a membrane pump and the energy of another concentration. Excitable cells like neurons and muscle cells.
Transport proteins move it across the membrane-ion channels. Click card to see definition. In the 1960s the Davson-Danielli model of membrane structure was widely accepted.
Transmission of electrical signals in nerve cells depends on rapid and controlled changes in the movement of sodium and potassium ions describe the excitation due to an electrical signal due to a stimulus. -Usually because molecules are too big or have a charge and can not go through the membrane alone. Explain what this means.
Biology questions and answers. His control experiment is two bodies of water separated by the same membrane but without the channel proteins. Describe what will pass EASILY through the membrane.
Click again to see term. A channel that allow membranes to be selectively permeable. 1 C hapter 5 Active Reading Guide Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling Section 1 1.
Tap card to see definition. Describe and give an example of a membrane channel a Membrane channels are a from BIO MISC at Fortis College Indianapolis. The currently accepted model of the membrane is.
Related to Essential Skill 3-4 3. Biophysicists measuring the electric current passing through cell membranes have found that in general cell membranes have a vastly greater electrical conductance than does a membrane bilayer composed only of phospholipids and sterols. Describe and give an example of a membrane channel a.
Protein tunnels allow ions to pass through them. More specifically channel proteins help molecules across the membrane via passive transport a process called facilitated. Describe the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure.
Membrane also cç Describe how each of the following can affect membrane fluidity. Up to 24 cash back membrane. Why do these molecules have a harder time.
He pours salt in one of the bodies of water. 3 Describe and give an example of a membrane channel. How is O2 moved across the cell membrane.
Click card to see definition. - ATP binding domains are called ATP-binding cassettes ABC - P-loop NTPases. - 2 membrane spanning domains and two ATP-binding domains.
Give an example of the importance of ion channels -eg. Phospholipids with unsaturated hydrocarbon chains membrane more live c.

Channel Protein Definition Function Examples Biology Dictionary
The Action Potential Anatomy And Physiology I
Comments
Post a Comment